NextGen 2024: Refractory SJIA & MAS Session Part 3
 AI Summary
AI Summary
Key Insights
- The REAL-HLH study assessed clinical and demographic characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes in patients treated with emapalumab in the US.
- The study focuses on emapalumab treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) secondary to Still's disease (sJIA/AOSD).
- Median time to achieving defined laboratory criteria ranged from 7 to 29.0 days.
- Overall survival and 12-month survival probability from emapalumab initiation was 90%.
- Four of 10 (40%) patients were considered for HSCT and of these, 1/4 (25%) received transplant
Loading...

Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

Loading...

Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

Loading...
![REAL-HLH Study Group (Investigators)
19
Dr. Allyson Hays [CHILDREN’S MERCY HOSPITALS AND CLINICS]
Dr. Anand Tandra [FRANCISCAN HEALTH]
Dr. Anish Ray [COOK CHILDREN’S MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Arun Panigrahi [UC DAVIS MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Ashley Hinson [CAROLINAS MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Ashley Baker [UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER]
Dr. Blachy Davila Saldana [CHILDREN'S NATIONAL MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Brant Ward [CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF RICHMOND AT VCU]
Dr. Carl Allen [TEXAS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL]
Drs. Deepika Bhatla & Lauren Draper [ST. LOUIS UNIVERSITY]
Dr. Diaz Gidvani [METHODIST CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL]
Dr. Edward Behrens [CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA]
Dr. Hilary Haines [CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF ALABAMA]
Dr. Jennifer Rothman [DUKE UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Joanna Weinstein [ANN AND ROBERT H. LURIE CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL]
Dr. John Carter [OREGON HEALTH AND SCIENCE UNIVERSITY]
Dr. May Chien [LUCILE PACKARD CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL AT STANFORD UNIVERSITY]
Dr. Michael Henry [PHOENIX CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL]
Dr. Michael Isakoff [CONNECTICUT CHILDREN'S MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Michael Jordan [CINCINNATI CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Michelle Hermiston [UCSF MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Mona Riskalla [UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Nicholas Gloude [RADY CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL]
Dr. Prakesh Satwani [NEW YORK PRESBYTERIAN HOSPITAL]
Dr. Rabi Hanna [CLEVELAND CLINIC]
Dr. Renee Modica [UF HEALTH SHANDS HOSPITAL]
Dr. Robert Cooper [BELLFLOWER MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Sachit Patel [UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA MEDICAL CENTER]
Dr. Shanmuganathan Chandrakasan [CHILDREN'S HEALTHCARE OF ATLANTA]
Dr. Sima Bhatt [WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY]
Dr. Stefanos Intzes [PROVIDENCE SACRED HEART MEDICAL CENTER & CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL]
Dr. Susmita Sarangi [GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL-MEDSTAR]
Dr. Taizo Nakano [CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL COLORADO]](https://d2z384uprhdr6y.cloudfront.net/qNrmvnBlblwondUMyLcivdOY-2R7o_AlDzp2PtyWyW0/rt:fill/q:100/w:1280/h:0/gravity:sm/czM6Ly9qYXVudC1wcm9kdWN0aW9uLXVwbG9hZHMvMjAyNC8xMi8wMy9mN2FmMTIwZi02NjVjLTQxYjQtOTc3ZS03YWRiZDQ2OWY1ZTcvc2xpZGVfMTktbC53ZWJw.webp)
Loading...

Loading...
NextGen 2024: Refractory SJIA & MAS Session Part 3
- 1. TREATMENT PATTERNS AND OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS WITH MACROPHAGE ACTIVATION SYNDROME SECONDARY TO STILL’S DISEASE TREATED WITH EMAPALUMAB Edward M. Behrens, MD Joseph Lee Hollander Chair in Pediatric Rheumatology Chief, Division of Rheumatology The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine at The University of Pennsylvania
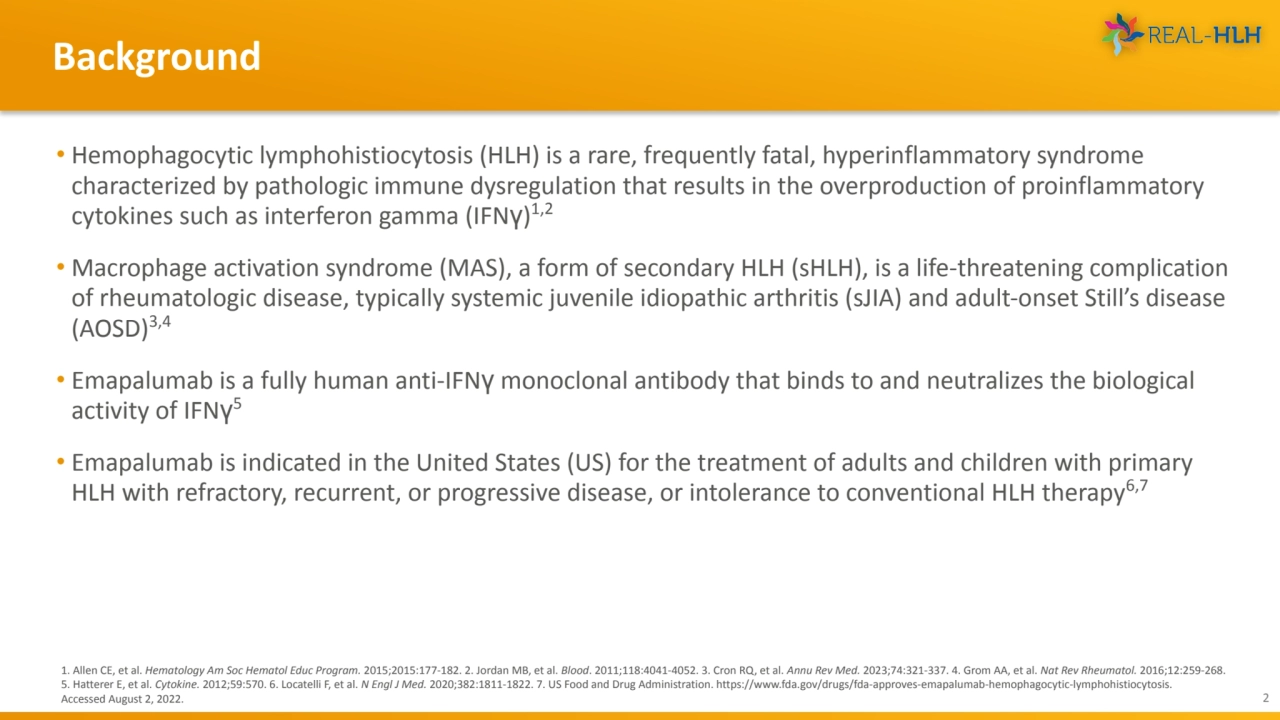
- 2. • Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare, frequently fatal, hyperinflammatory syndrome characterized by pathologic immune dysregulation that results in the overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines such as interferon gamma (IFNγ) 1,2 • Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), a form of secondary HLH (sHLH), is a life-threatening complication of rheumatologic disease, typically systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD)3,4 • Emapalumab is a fully human anti-IFNγ monoclonal antibody that binds to and neutralizes the biological activity of IFNγ 5 • Emapalumab is indicated in the United States (US) for the treatment of adults and children with primary HLH with refractory, recurrent, or progressive disease, or intolerance to conventional HLH therapy6,7 Background 2 1. Allen CE, et al. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015;2015:177-182. 2. Jordan MB, et al. Blood. 2011;118:4041-4052. 3. Cron RQ, et al. Annu Rev Med. 2023;74:321-337. 4. Grom AA, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:259-268. 5. Hatterer E, et al. Cytokine. 2012;59:570. 6. Locatelli F, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1811-1822. 7. US Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-approves-emapalumab-hemophagocytic-lymphohistiocytosis. Accessed August 2, 2022.
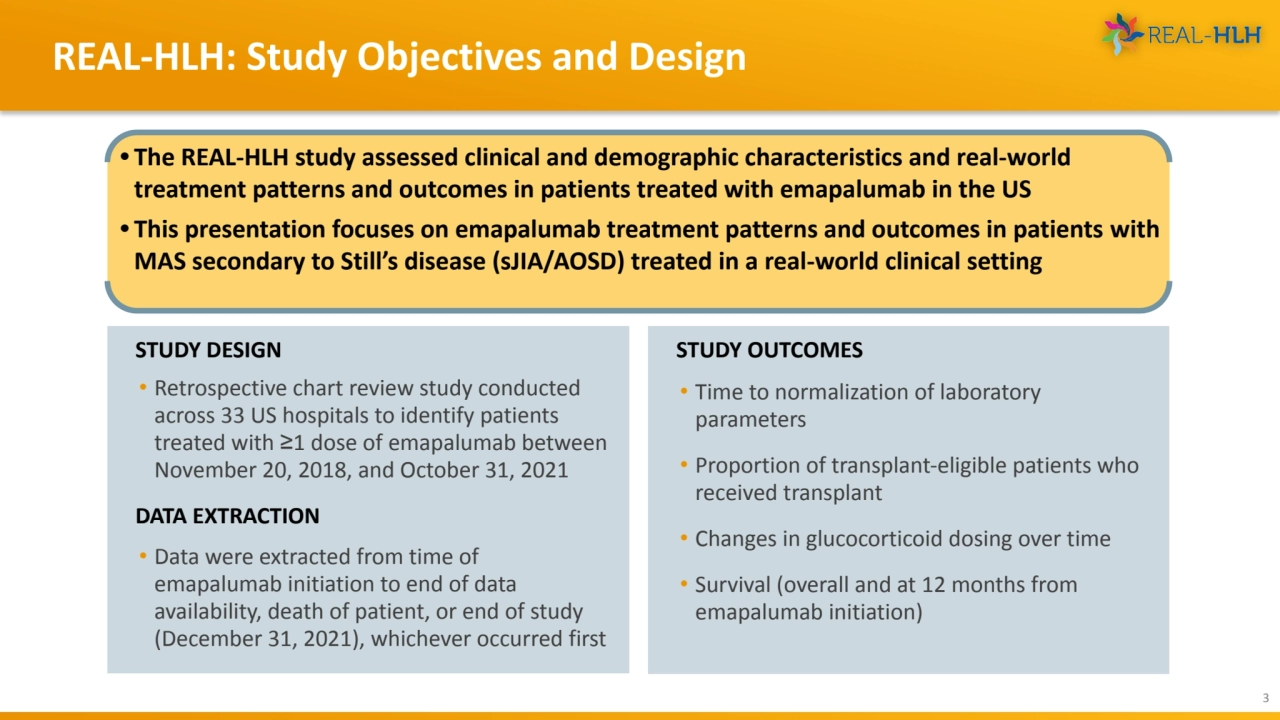
- 3. REAL-HLH: Study Objectives and Design 3 • The REAL-HLH study assessed clinical and demographic characteristics and real-world treatment patterns and outcomes in patients treated with emapalumab in the US • This presentation focuses on emapalumab treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with MAS secondary to Still’s disease (sJIA/AOSD) treated in a real-world clinical setting STUDY DESIGN • Retrospective chart review study conducted across 33 US hospitals to identify patients treated with ≥1 dose of emapalumab between November 20, 2018, and October 31, 2021 DATA EXTRACTION • Data were extracted from time of emapalumab initiation to end of data availability, death of patient, or end of study (December 31, 2021), whichever occurred first STUDY OUTCOMES • Time to normalization of laboratory parameters • Proportion of transplant-eligible patients who received transplant • Changes in glucocorticoid dosing over time • Survival (overall and at 12 months from emapalumab initiation)
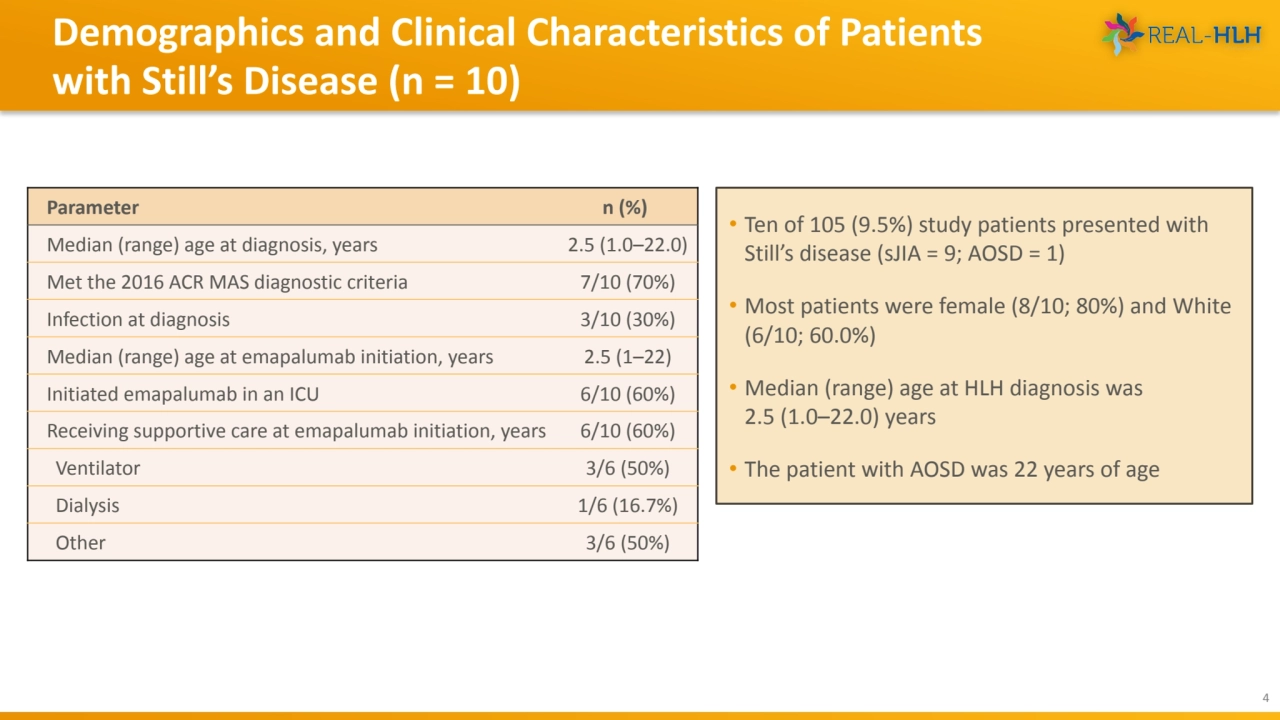
- 4. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Still’s Disease (n = 10) 4 • Ten of 105 (9.5%) study patients presented with Still’s disease (sJIA = 9; AOSD = 1) • Most patients were female (8/10; 80%) and White (6/10; 60.0%) • Median (range) age at HLH diagnosis was 2.5 (1.0–22.0) years • The patient with AOSD was 22 years of age Parameter n (%) Median (range) age at diagnosis, years 2.5 (1.0–22.0) Met the 2016 ACR MAS diagnostic criteria 7/10 (70%) Infection at diagnosis 3/10 (30%) Median (range) age at emapalumab initiation, years 2.5 (1–22) Initiated emapalumab in an ICU 6/10 (60%) Receiving supportive care at emapalumab initiation, years 6/10 (60%) Ventilator 3/6 (50%) Dialysis 1/6 (16.7%) Other 3/6 (50%)
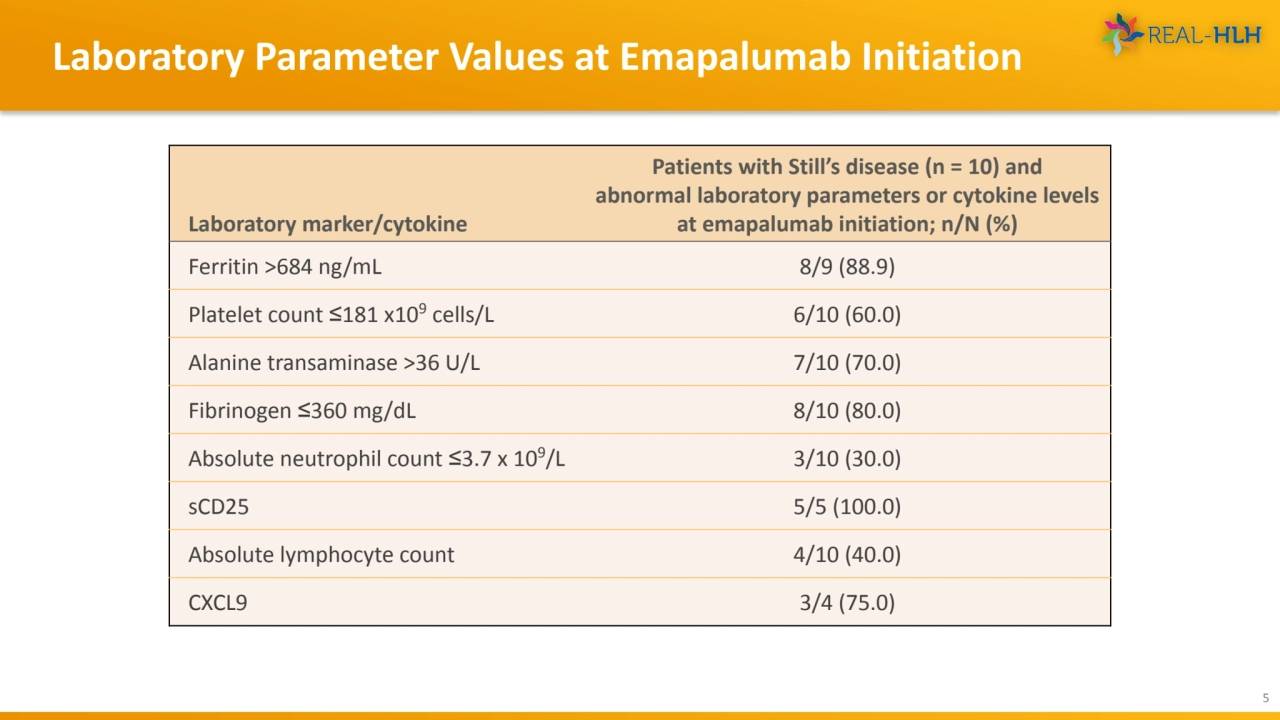
- 5. Laboratory Parameter Values at Emapalumab Initiation 5 Laboratory marker/cytokine Patients with Still’s disease (n = 10) and abnormal laboratory parameters or cytokine levels at emapalumab initiation; n/N (%) Ferritin >684 ng/mL 8/9 (88.9) Platelet count ≤181 x109 cells/L 6/10 (60.0) Alanine transaminase >36 U/L 7/10 (70.0) Fibrinogen ≤360 mg/dL 8/10 (80.0) Absolute neutrophil count ≤3.7 x 109/L 3/10 (30.0) sCD25 5/5 (100.0) Absolute lymphocyte count 4/10 (40.0) CXCL9 3/4 (75.0)
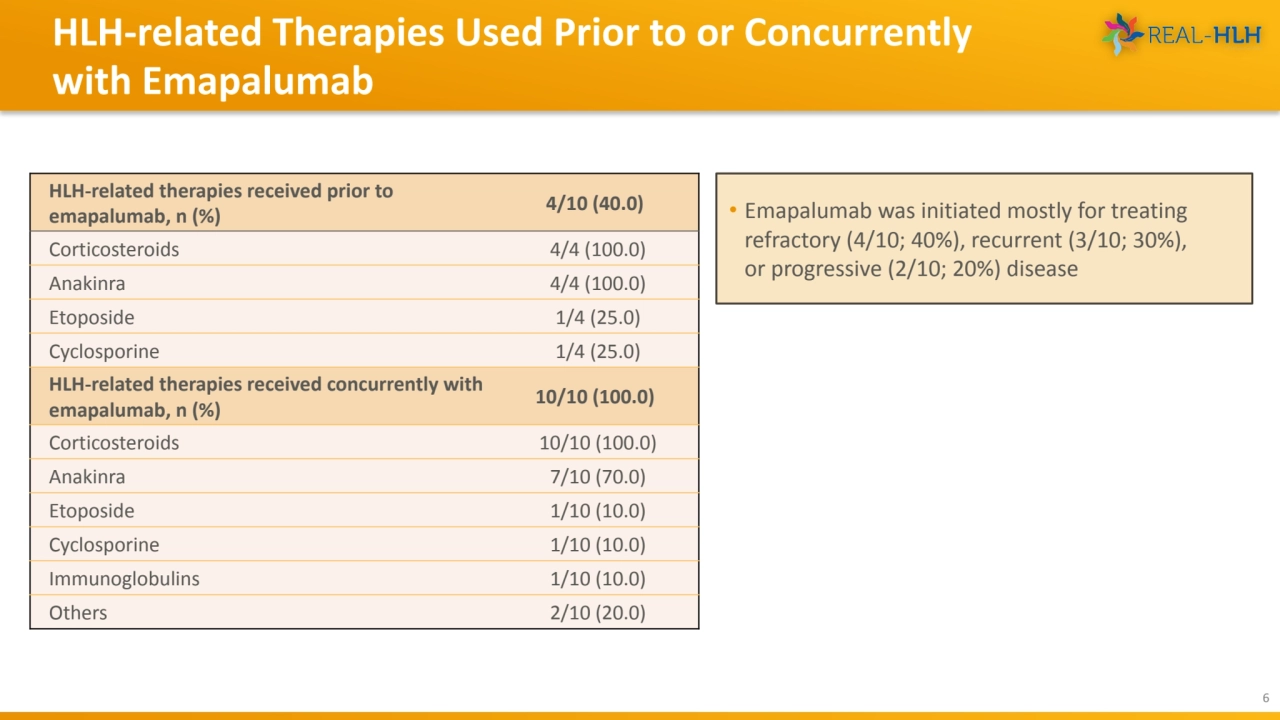
- 6. HLH-related Therapies Used Prior to or Concurrently with Emapalumab 6 • Emapalumab was initiated mostly for treating refractory (4/10; 40%), recurrent (3/10; 30%), or progressive (2/10; 20%) disease HLH-related therapies received prior to emapalumab, n (%) 4/10 (40.0) Corticosteroids 4/4 (100.0) Anakinra 4/4 (100.0) Etoposide 1/4 (25.0) Cyclosporine 1/4 (25.0) HLH-related therapies received concurrently with emapalumab, n (%) 10/10 (100.0) Corticosteroids 10/10 (100.0) Anakinra 7/10 (70.0) Etoposide 1/10 (10.0) Cyclosporine 1/10 (10.0) Immunoglobulins 1/10 (10.0) Others 2/10 (20.0)
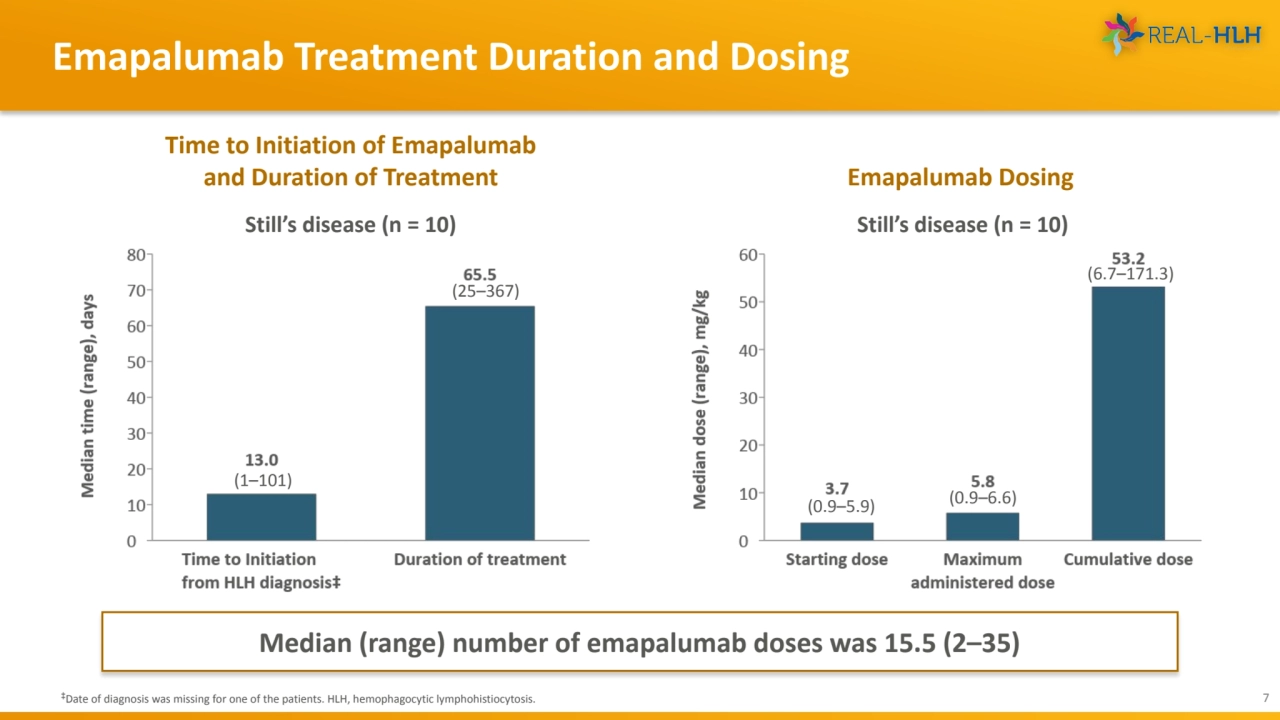
- 7. Emapalumab Treatment Duration and Dosing 7 ‡Date of diagnosis was missing for one of the patients. HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Emapalumab Dosing Time to Initiation of Emapalumab and Duration of Treatment (1–101) (25–367) Still’s disease (n = 10) Median (range) number of emapalumab doses was 15.5 (2–35) Still’s disease (n = 10) (0.9–5.9) (0.9–6.6) (6.7–171.3)
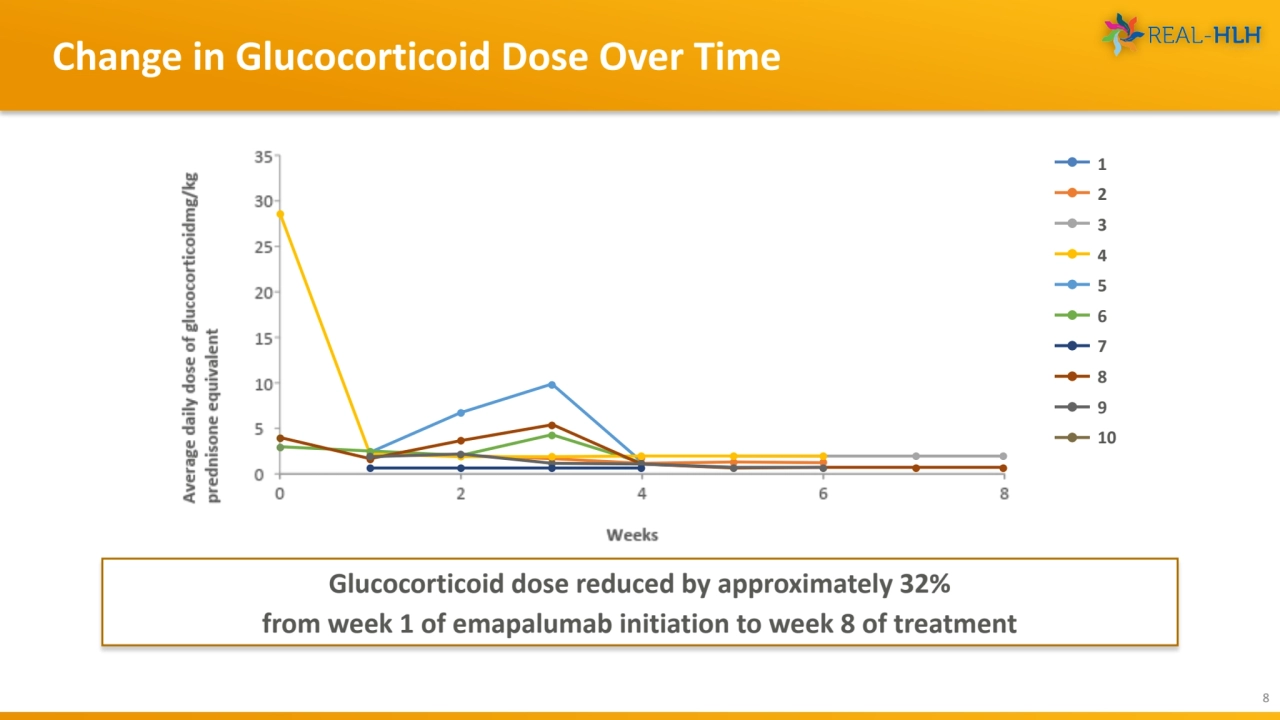
- 8. Change in Glucocorticoid Dose Over Time 8 Glucocorticoid dose reduced by approximately 32% from week 1 of emapalumab initiation to week 8 of treatment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
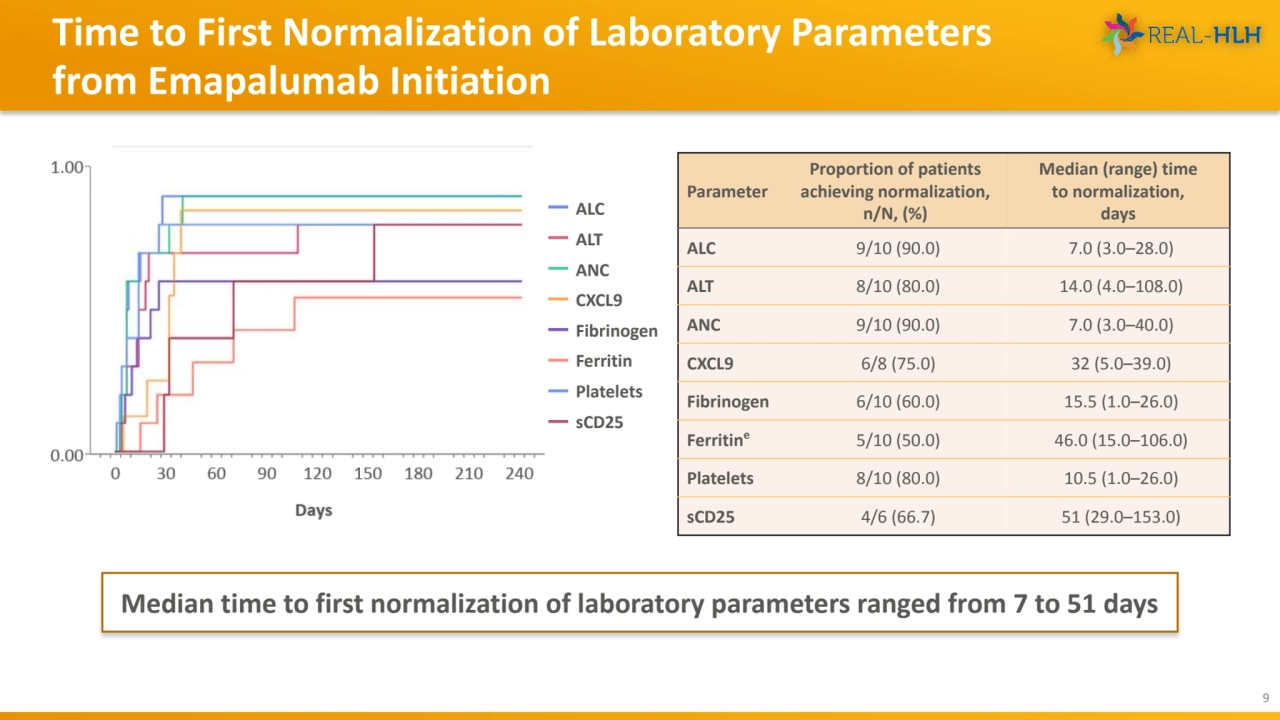
- 9. Time to First Normalization of Laboratory Parameters from Emapalumab Initiation 9 Median time to first normalization of laboratory parameters ranged from 7 to 51 days ALC ALT ANC CXCL9 Fibrinogen Ferritin Platelets sCD25 Parameter Proportion of patients achieving normalization, n/N, (%) Median (range) time to normalization, days ALC 9/10 (90.0) 7.0 (3.0–28.0) ALT 8/10 (80.0) 14.0 (4.0–108.0) ANC 9/10 (90.0) 7.0 (3.0–40.0) CXCL9 6/8 (75.0) 32 (5.0–39.0) Fibrinogen 6/10 (60.0) 15.5 (1.0–26.0) Ferritine 5/10 (50.0) 46.0 (15.0–106.0) Platelets 8/10 (80.0) 10.5 (1.0–26.0) sCD25 4/6 (66.7) 51 (29.0–153.0)
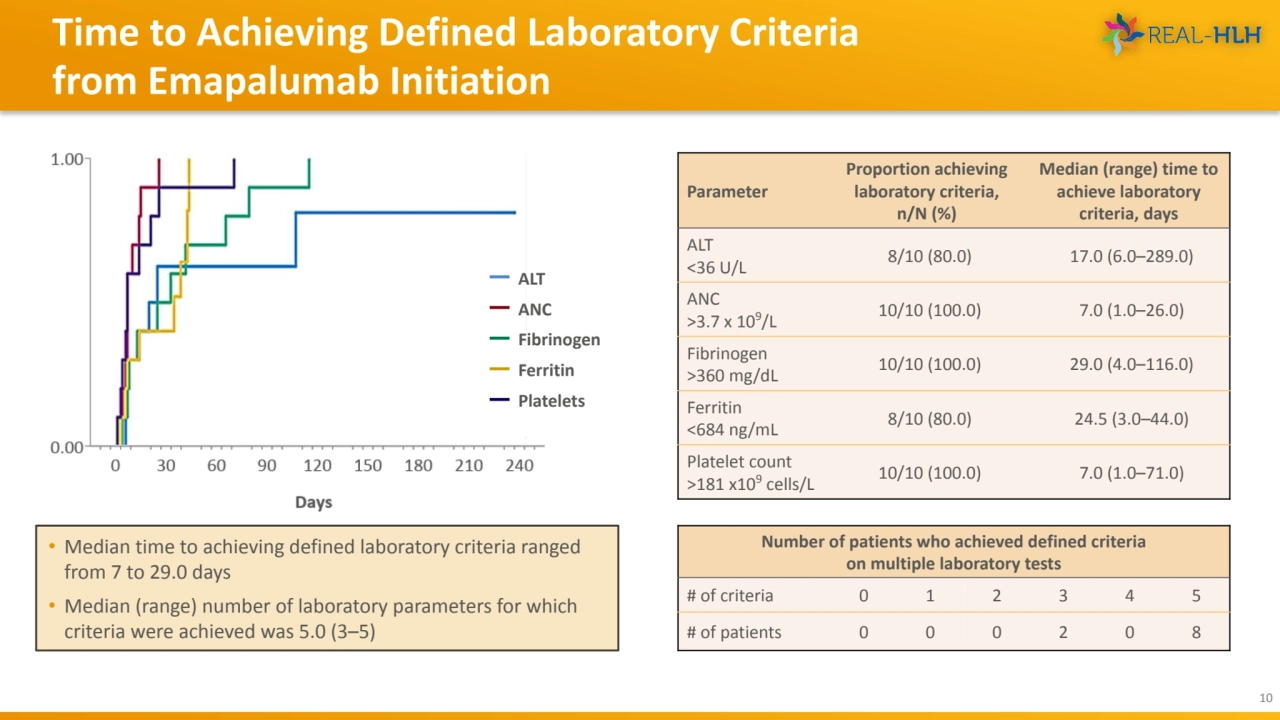
- 10. Time to Achieving Defined Laboratory Criteria from Emapalumab Initiation 10 Parameter Proportion achieving laboratory criteria, n/N (%) Median (range) time to achieve laboratory criteria, days ALT <36 U/L 8/10 (80.0) 17.0 (6.0–289.0) ANC >3.7 x 109/L 10/10 (100.0) 7.0 (1.0–26.0) Fibrinogen >360 mg/dL 10/10 (100.0) 29.0 (4.0–116.0) Ferritin <684 ng/mL 8/10 (80.0) 24.5 (3.0–44.0) Platelet count >181 x109 cells/L 10/10 (100.0) 7.0 (1.0–71.0) ALT ANC Fibrinogen Ferritin Platelets • Median time to achieving defined laboratory criteria ranged from 7 to 29.0 days • Median (range) number of laboratory parameters for which criteria were achieved was 5.0 (3–5) Number of patients who achieved defined criteria on multiple laboratory tests # of criteria 0 1 2 3 4 5 # of patients 0 0 0 2 0 8
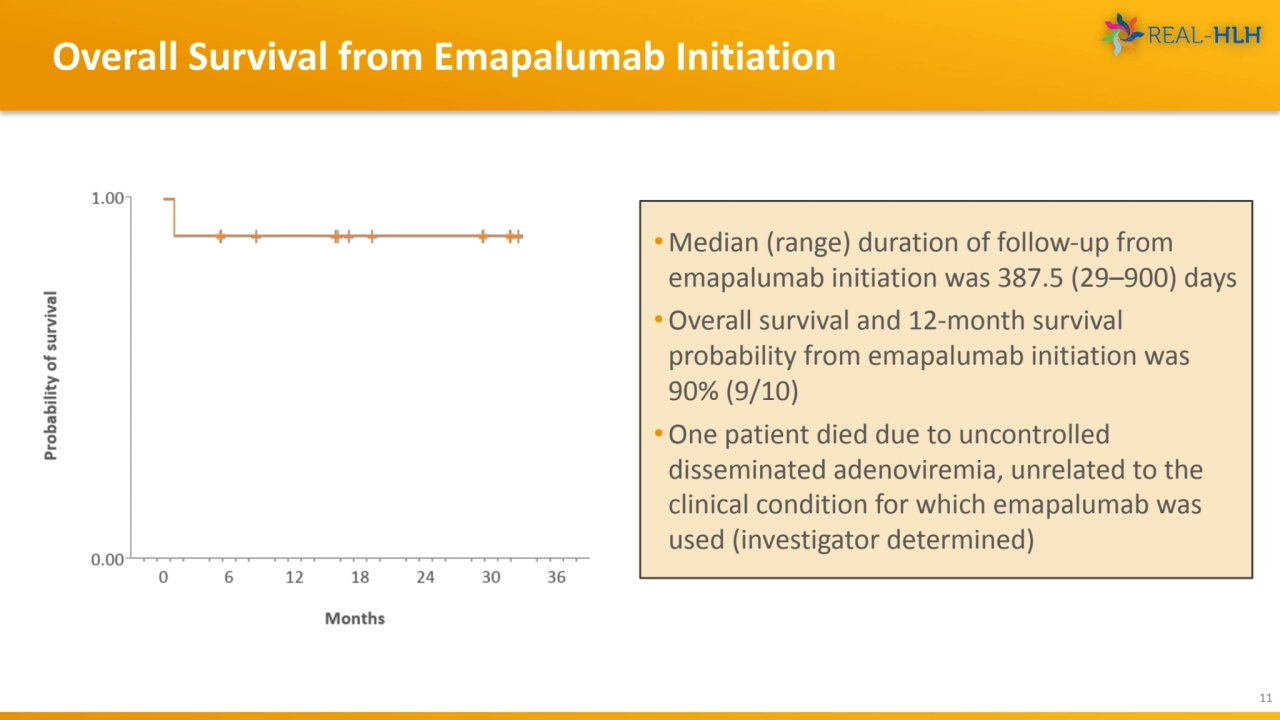
- 11. Overall Survival from Emapalumab Initiation 11 • Median (range) duration of follow-up from emapalumab initiation was 387.5 (29–900) days •Overall survival and 12-month survival probability from emapalumab initiation was 90% (9/10) •One patient died due to uncontrolled disseminated adenoviremia, unrelated to the clinical condition for which emapalumab was used (investigator determined)
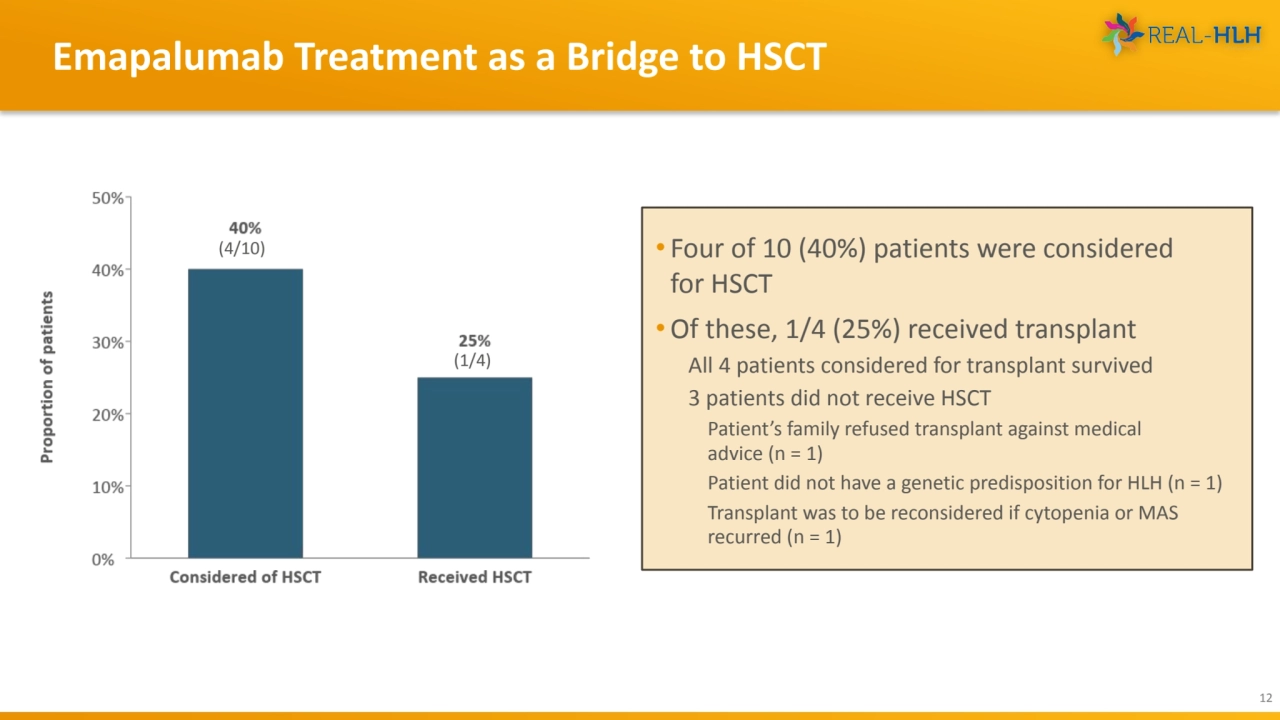
- 12. Emapalumab Treatment as a Bridge to HSCT 12 (1/4) (4/10) • Four of 10 (40%) patients were considered for HSCT •Of these, 1/4 (25%) received transplant All 4 patients considered for transplant survived 3 patients did not receive HSCT Patient’s family refused transplant against medical advice (n = 1) Patient did not have a genetic predisposition for HLH (n = 1) Transplant was to be reconsidered if cytopenia or MAS recurred (n = 1)
- 13. • As with other retrospective chart review studies, data may not be uniformly available across all treatment centers; therefore, there is a risk of missing or incomplete information • Given that emapalumab is indicated as second-line treatment, there is a risk of bias towards patients with poor prognosis • Other limitations include an inability to comprehensively evaluate treatment response due to data gaps (limited availability and lack of uniformity in the timing of assessment of laboratory values, no visual analog scale etc.) • Safety-related data were not collected or evaluated • Given the limited sample size of the study, results may not be generalizable beyond the study patients Limitations 13
- 14. • This is the first study to report real-world treatment patterns and outcomes among patients with MAS secondary to Still’s disease who received treatment with emapalumab • Glucocorticoid dose reduced by approximately 32% from week 1 of emapalumab initiation to week 8 • Overall survival and 12-month survival probability from emapalumab initiation was 90.0% Conclusions 14
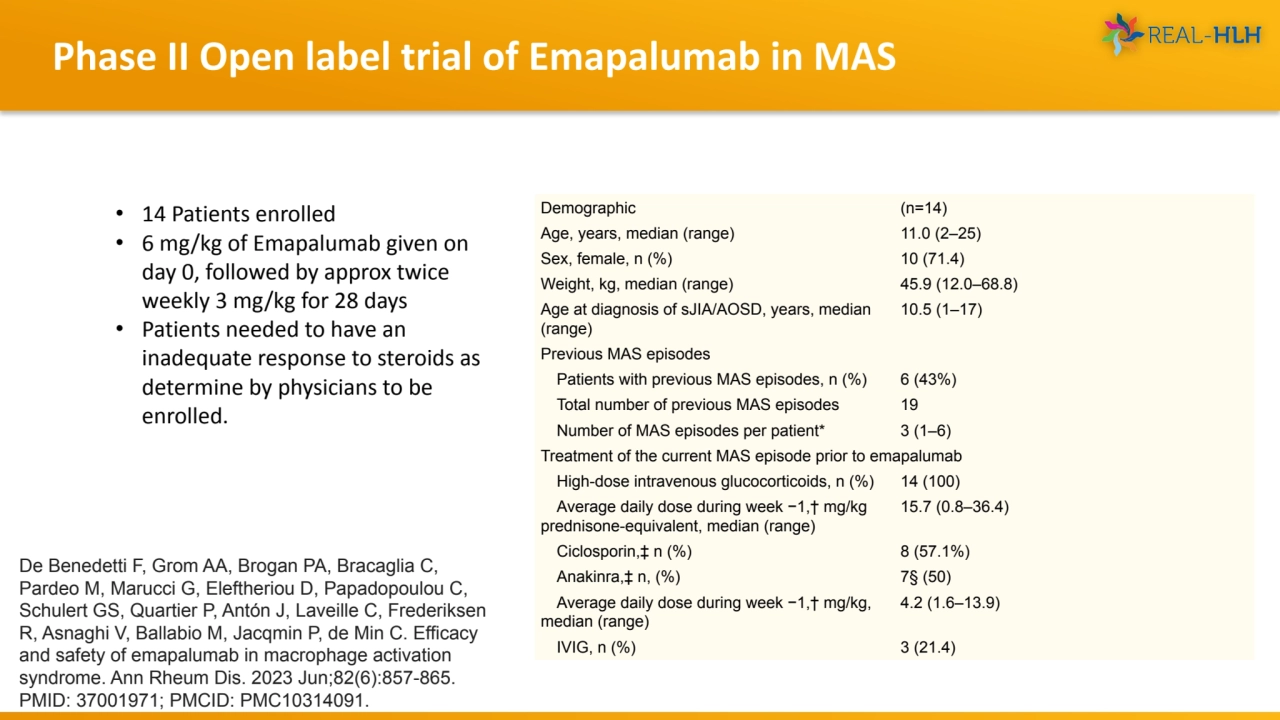
- 15. Phase II Open label trial of Emapalumab in MAS Demographic (n=14) Age, years, median (range) 11.0 (2–25) Sex, female, n (%) 10 (71.4) Weight, kg, median (range) 45.9 (12.0–68.8) Age at diagnosis of sJIA/AOSD, years, median (range) 10.5 (1–17) Previous MAS episodes Patients with previous MAS episodes, n (%) 6 (43%) Total number of previous MAS episodes 19 Number of MAS episodes per patient* 3 (1–6) Treatment of the current MAS episode prior to emapalumab High-dose intravenous glucocorticoids, n (%) 14 (100) Average daily dose during week −1,† mg/kg prednisone-equivalent, median (range) 15.7 (0.8–36.4) Ciclosporin,‡ n (%) 8 (57.1%) Anakinra,‡ n, (%) 7§ (50) Average daily dose during week −1,† mg/kg, median (range) 4.2 (1.6–13.9) IVIG, n (%) 3 (21.4) De Benedetti F, Grom AA, Brogan PA, Bracaglia C, Pardeo M, Marucci G, Eleftheriou D, Papadopoulou C, Schulert GS, Quartier P, Antón J, Laveille C, Frederiksen R, Asnaghi V, Ballabio M, Jacqmin P, de Min C. Efficacy and safety of emapalumab in macrophage activation syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Jun;82(6):857-865. PMID: 37001971; PMCID: PMC10314091. • 14 Patients enrolled • 6 mg/kg of Emapalumab given on day 0, followed by approx twice weekly 3 mg/kg for 28 days • Patients needed to have an inadequate response to steroids as determine by physicians to be enrolled.
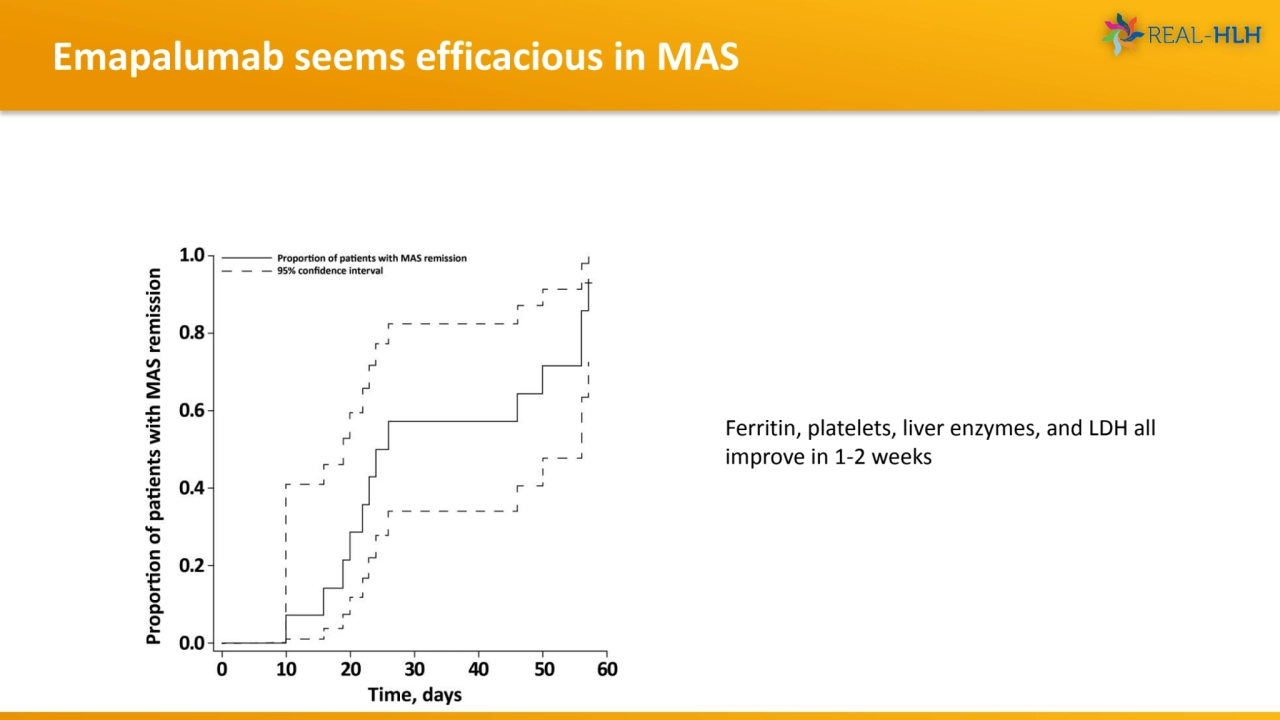
- 16. Emapalumab seems efficacious in MAS Ferritin, platelets, liver enzymes, and LDH all improve in 1-2 weeks
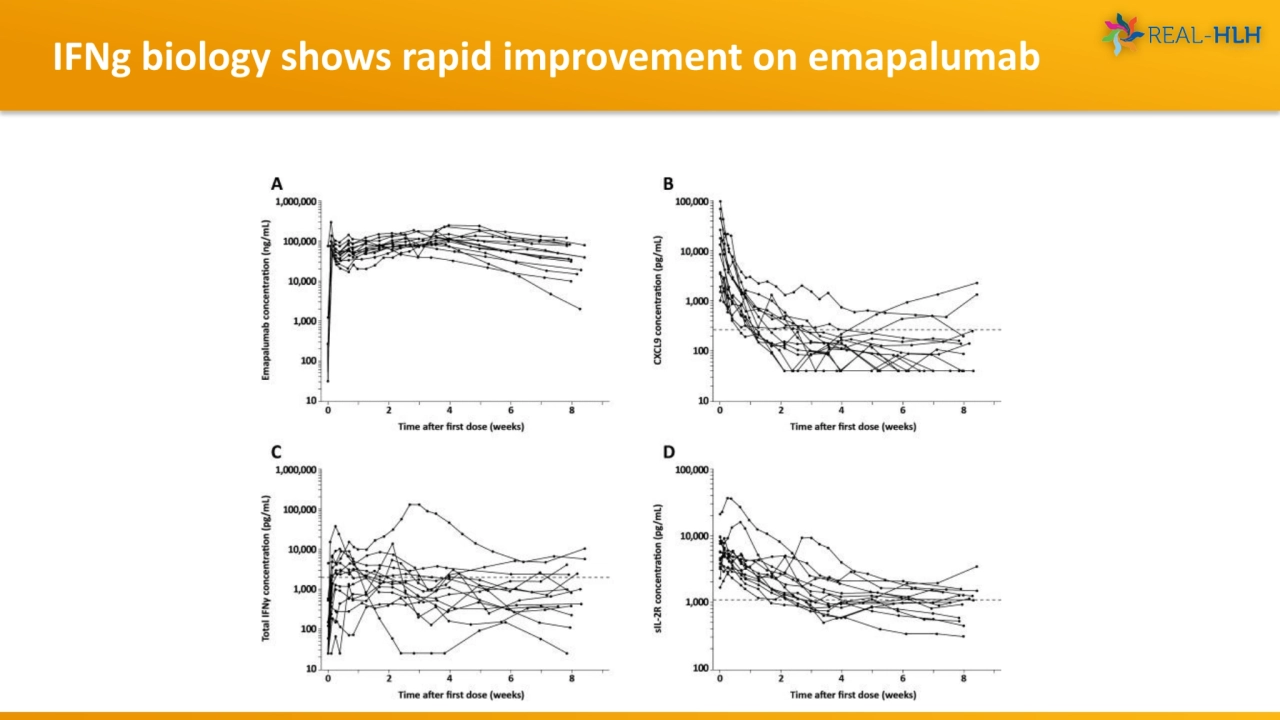
- 17. IFNg biology shows rapid improvement on emapalumab
- 18. Conclusions • Emapalumab has significant real world use experience as well as clinical trial evidence for SJIA-MAS • Placebo controlled data, either as primary treatment or withdrawal, is lacking • The fundamental biology and the existing data support the notion that this therapy may be an important part of the armamentarium in refractory disease 18
- 19. REAL-HLH Study Group (Investigators) 19 Dr. Allyson Hays [CHILDREN’S MERCY HOSPITALS AND CLINICS] Dr. Anand Tandra [FRANCISCAN HEALTH] Dr. Anish Ray [COOK CHILDREN’S MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Arun Panigrahi [UC DAVIS MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Ashley Hinson [CAROLINAS MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Ashley Baker [UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER] Dr. Blachy Davila Saldana [CHILDREN'S NATIONAL MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Brant Ward [CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF RICHMOND AT VCU] Dr. Carl Allen [TEXAS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL] Drs. Deepika Bhatla & Lauren Draper [ST. LOUIS UNIVERSITY] Dr. Diaz Gidvani [METHODIST CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL] Dr. Edward Behrens [CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA] Dr. Hilary Haines [CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF ALABAMA] Dr. Jennifer Rothman [DUKE UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Joanna Weinstein [ANN AND ROBERT H. LURIE CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL] Dr. John Carter [OREGON HEALTH AND SCIENCE UNIVERSITY] Dr. May Chien [LUCILE PACKARD CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL AT STANFORD UNIVERSITY] Dr. Michael Henry [PHOENIX CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL] Dr. Michael Isakoff [CONNECTICUT CHILDREN'S MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Michael Jordan [CINCINNATI CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Michelle Hermiston [UCSF MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Mona Riskalla [UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Nicholas Gloude [RADY CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL] Dr. Prakesh Satwani [NEW YORK PRESBYTERIAN HOSPITAL] Dr. Rabi Hanna [CLEVELAND CLINIC] Dr. Renee Modica [UF HEALTH SHANDS HOSPITAL] Dr. Robert Cooper [BELLFLOWER MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Sachit Patel [UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA MEDICAL CENTER] Dr. Shanmuganathan Chandrakasan [CHILDREN'S HEALTHCARE OF ATLANTA] Dr. Sima Bhatt [WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY] Dr. Stefanos Intzes [PROVIDENCE SACRED HEART MEDICAL CENTER & CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL] Dr. Susmita Sarangi [GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL-MEDSTAR] Dr. Taizo Nakano [CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL COLORADO]
- 20. 20 Appendix
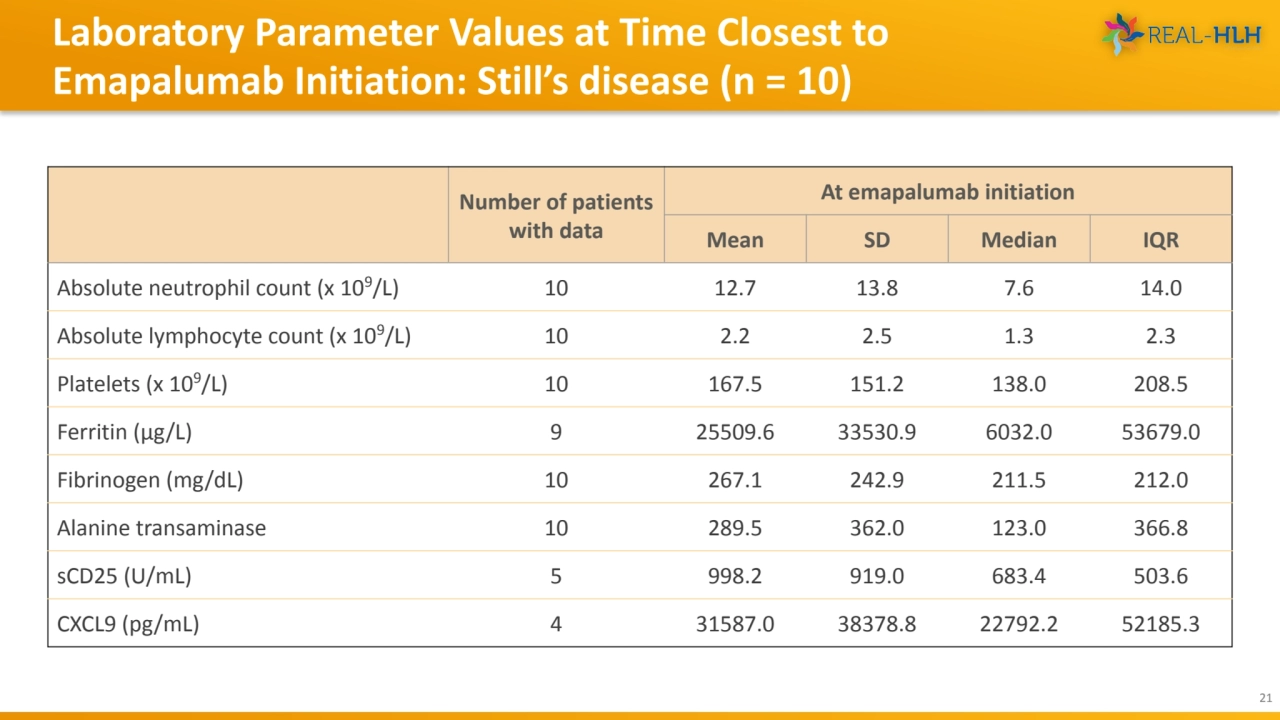
- 21. Laboratory Parameter Values at Time Closest to Emapalumab Initiation: Still’s disease (n = 10) 21 Number of patients with data At emapalumab initiation Mean SD Median IQR Absolute neutrophil count (x 109/L) 10 12.7 13.8 7.6 14.0 Absolute lymphocyte count (x 109/L) 10 2.2 2.5 1.3 2.3 Platelets (x 109/L) 10 167.5 151.2 138.0 208.5 Ferritin (μg/L) 9 25509.6 33530.9 6032.0 53679.0 Fibrinogen (mg/dL) 10 267.1 242.9 211.5 212.0 Alanine transaminase 10 289.5 362.0 123.0 366.8 sCD25 (U/mL) 5 998.2 919.0 683.4 503.6 CXCL9 (pg/mL) 4 31587.0 38378.8 22792.2 52185.3