NextGen 2024: Unmet Needs & Clinical Trial Challenges Session Part 1
 AI Summary
AI Summary
Key Insights
- Around 20% of SJIA patients develop a refractory disease course despite IL-1 and IL-6 blocking agents.
- Refractory SJIA can present with different clinical patterns, including relapsing MAS, which may involve liver involvement.
- Patients with SJIA and relapsing MAS appear to be at risk for SJIA-associated lung disease.
- Liver biopsies of patients with SJIA and relapsing MAS often show elevated liver enzymes and characteristic inflammatory infiltrates.
- Challenges in clinical trials for smoldering MAS include not fully meeting criteria for MAS and difficulties with eligibility due to systemic features or background medications.
Loading...

Loading...

Loading...
Loading...

Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

Loading...

Loading...

NextGen 2024: Unmet Needs & Clinical Trial Challenges Session Part 1
- 1. SJIA with relapsing MAS Alexei Grom, MD Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center NextGen Therapies in SJIA, Still’s & MAS Washington DC November 13-15
- 2. SJIA with refractory course • Despite recently approved IL-1 and IL-6 blocking agents, about 20% of patients with SJIA develop a refractory disease course • fail to respond to all the approved biologic and non-biologic DMARDs • persistent disease activity requiring maintenance therapy with glucocorticoids • Several distinct clinical patterns of refractory disease • Refractory SJIA with predominantly persistent arthritis • Refractory SJIA with predominantly systemic features • SJIA with chronic parenchymal lung disease • SJIA with relapsing MAS • Includes a subgroup with predominantly liver involvement • Most of these patients do not meet eligibility criteria in the ongoing clinical trials in SJIA Erkens et al, Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2021;47:585
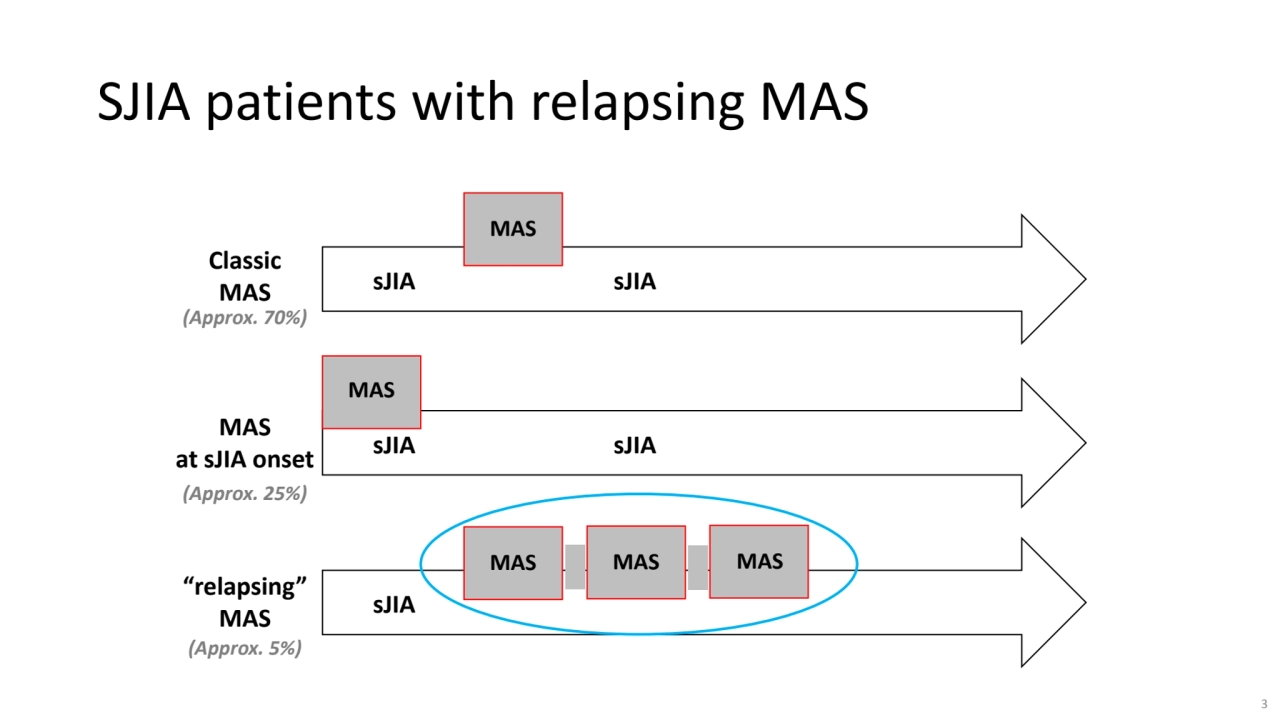
- 3. sJIA sJIA MAS sJIA sJIA MAS sJIA MAS MAS MAS Classic MAS MAS at sJIA onset “relapsing” MAS (Approx. 70%) (Approx. 25%) (Approx. 5%) SJIA patients with relapsing MAS 3
- 4. SJIA patients with relapsing MAS • These patients appear at risk for sJIA-associated lung disease • A large proportion of these patients have predominantly liver involvement 4
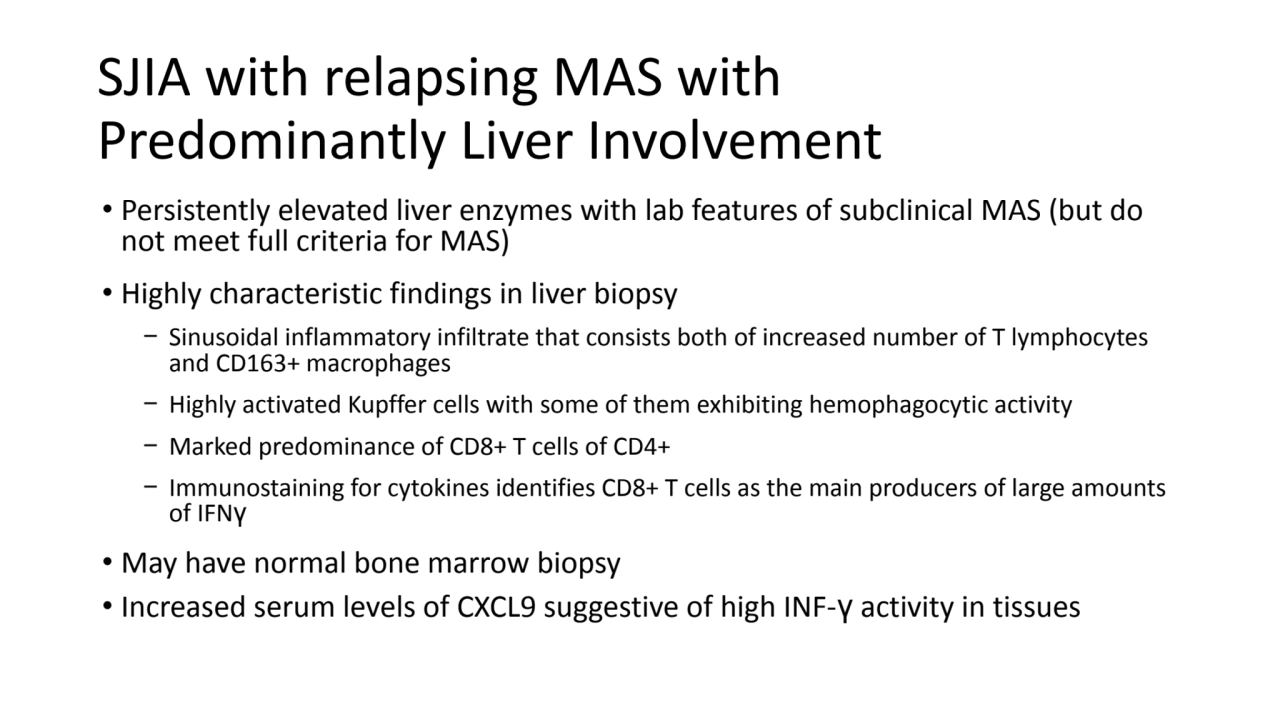
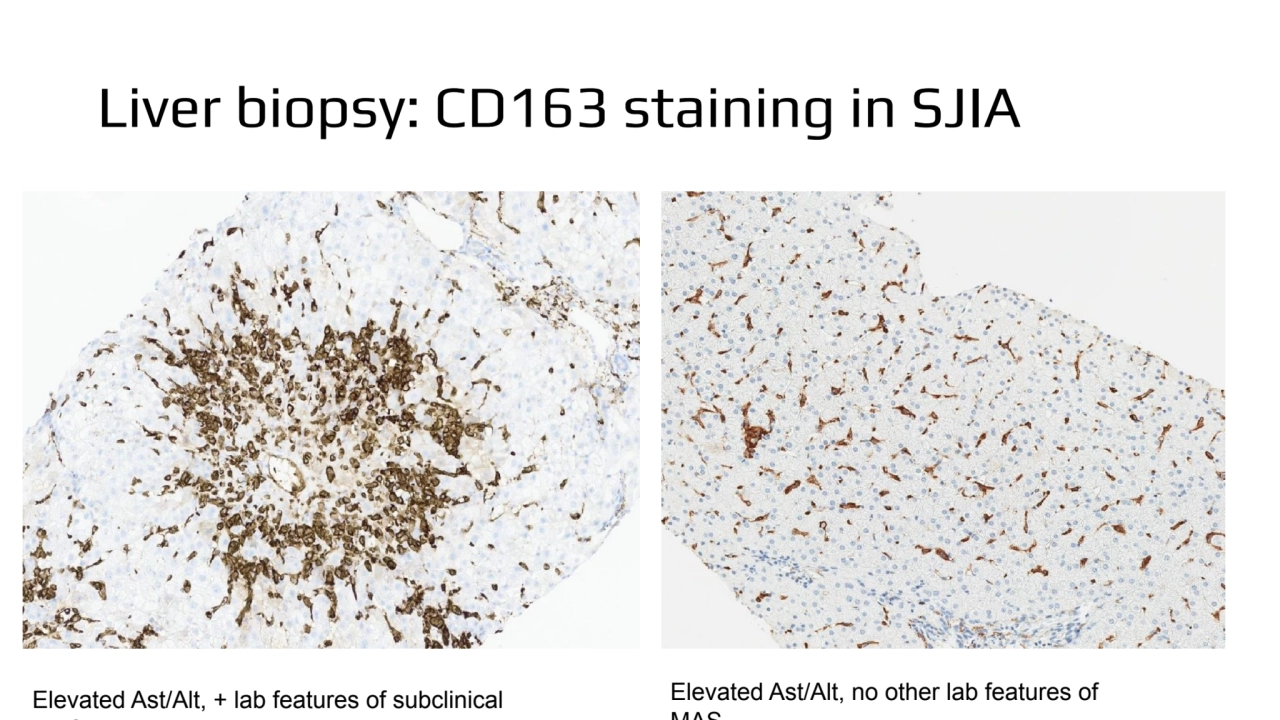
- 5. SJIA with relapsing MAS with Predominantly Liver Involvement • Persistently elevated liver enzymes with lab features of subclinical MAS (but do not meet full criteria for MAS) • Highly characteristic findings in liver biopsy − Sinusoidal inflammatory infiltrate that consists both of increased number of T lymphocytes and CD163+ macrophages − Highly activated Kupffer cells with some of them exhibiting hemophagocytic activity − Marked predominance of CD8+ T cells of CD4+ − Immunostaining for cytokines identifies CD8+ T cells as the main producers of large amounts of IFNγ • May have normal bone marrow biopsy • Increased serum levels of CXCL9 suggestive of high INF-γ activity in tissues
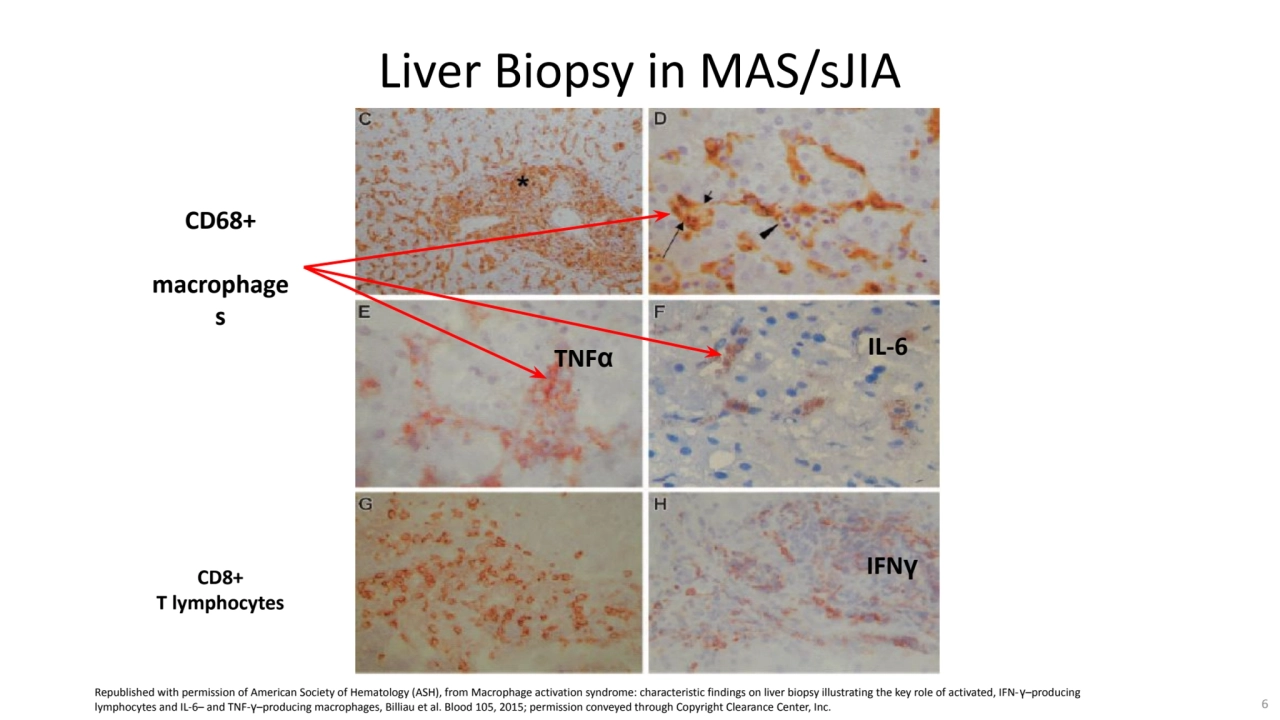
- 6. CD68+ macrophage s TNFα IL-6 IFNγ Liver Biopsy in MAS/sJIA CD8+ T lymphocytes Republished with permission of American Society of Hematology (ASH), from Macrophage activation syndrome: characteristic findings on liver biopsy illustrating the key role of activated, IFN-γ–producing lymphocytes and IL-6– and TNF-γ–producing macrophages, Billiau et al. Blood 105, 2015; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. 6
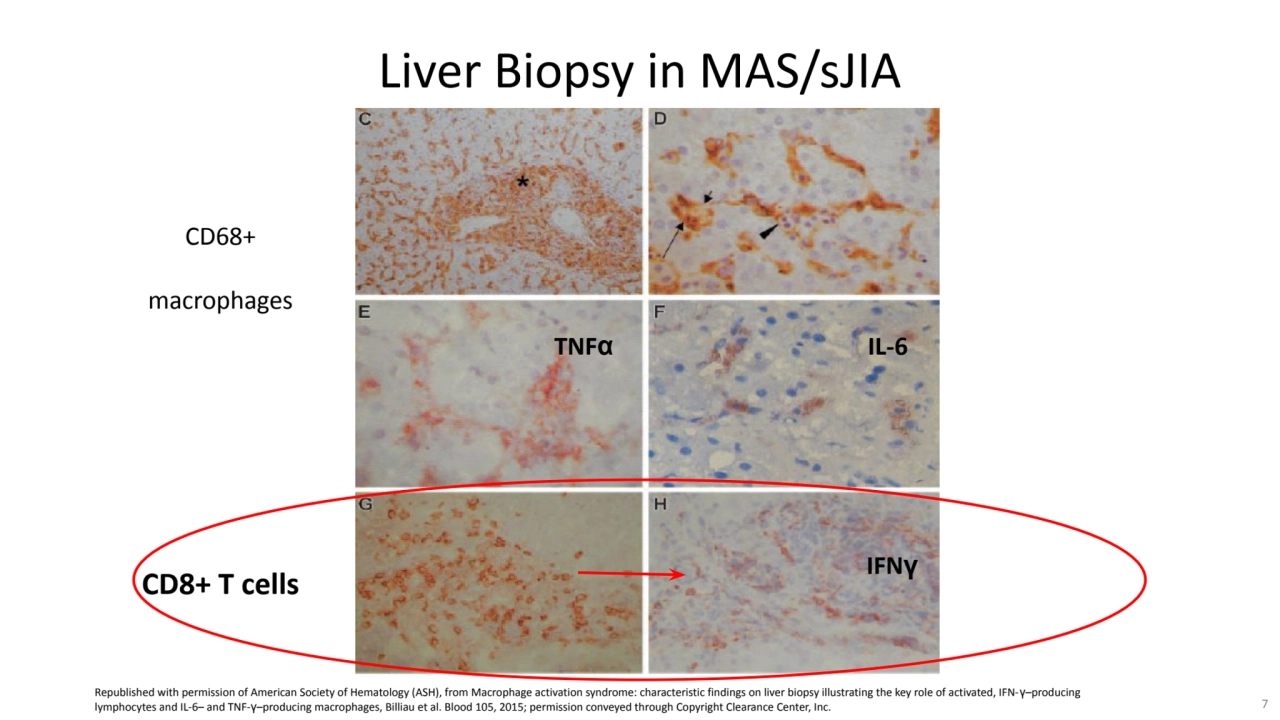
- 7. CD68+ macrophages Liver Biopsy in MAS/sJIA CD8+ T cells TNFα IL-6 IFNγ Republished with permission of American Society of Hematology (ASH), from Macrophage activation syndrome: characteristic findings on liver biopsy illustrating the key role of activated, IFN-γ–producing lymphocytes and IL-6– and TNF-γ–producing macrophages, Billiau et al. Blood 105, 2015; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. 7
- 8. Liver biopsy: CD163 staining in SJIA Elevated Ast/Alt, + lab features of subclinical MAS Elevated Ast/Alt, no other lab features of MAS
- 9. MAS with Predominantly Liver Involvement • Similar histologic pattern observed by Prencipe et al. in 3 patients (2 of whom fully met the ILAR criteria for sJIA): − Large numbers of portal/periportal CD68+ macrophages and T cells • Liver biopsies showed highly increased levels of mRNA for IFNγ-induced genes, while other classical pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-18, IL-6 and TNFα were not markedly increased − Type I IFN induced gene expression was also roughly normal Prencipe G et al. PLoS One 2019;14:e0226043. 9
- 10. MAS with Predominantly Liver Involvement •JAKi? • CyA? • MMF? • Emapalumab?
- 11. Challenges with clinical trials in ‘smoldering MAS” • Do not fully meet criteria for MAS • Not eligible for MAS trials • If predominantly systemic features • Due to the absence of arthritis cannot be dx as SJIA and are not eligible for ongoing SJIA trails • Due to the absence of genetic dx, cannot be enrolled in the ongoing trials in inflammasopathies (such as anti-IL18/IL1 therapeutics in NLRC4 GoF) • Outcome measures for systemic aspect of the disease are not well defined • Options are modifying ACR JIA measures, or using Autoinflammatory Disease Activity Index, or Systemic JADAS • No clear how to handle numerous background medications (most trials require withdrawal with variable washout periods)